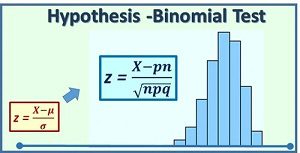
Binomial Test
A binomial test uses sample data to evaluate Hypothesis about the values of p and q for a population consisting of binomial data.
The measurement scale consists of exactly two categories
Each individual observation in a sample is classified in only one of the two categories
Sample data consist of the frequency or number of individuals in each category