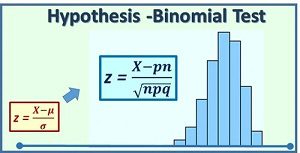
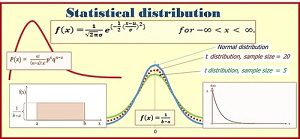
Vector Space : Question-1
Vector Space Let \(V\) be a set with cardinality at least 2 and let \((V,+)\) be an Abelian group with respect to the operation \(+\). Let \(\mathbb{R}\) be the field of real numbers. For any \(c\in\mathbb{R}\) and \(v\in V\), define \(c\cdot v = 0\), where \(0\) is the identity element in the Abelian group \((V,+)\). […]