Python library for graph plotting: Matplotlib
- Matplotlib is a plotting library for Python. It is used along with NumPy to provide an environment that is an effective open source alternative for MatLab.

- It can also be used with graphics toolkits like PyQt and wxPython.
- It was first written by John D. Hunter. Since 2012, Michael Droettboom is the principal developer.
- Conventionally, the package is imported into the Python script by adding the following statement:
pip install matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Graph Character description code

Plot Color: Character
Following formatting characters for color can be used.
Plot: X and Y- axis labels
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.xlabel('x-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y axis')Plot: Adding Title and Y- axis labels
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.xlabel('x-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y axis')
plt.title('frequency distribution')
Plot: Grid
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.xlabel('x-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y axis')
plt.title('frequency distribution')
plt.grid('true')Line Graph
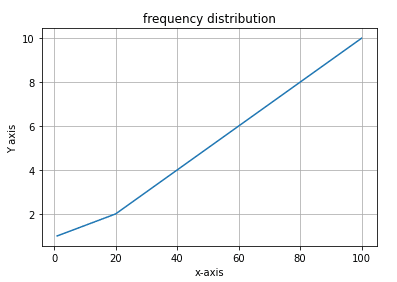
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.xlabel('x-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y axis')
plt.title('frequency distribution')
plt.grid('true')
x=(1,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100)
y=(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10)
plt.plot(x,y)Line Graph: Marker & line style
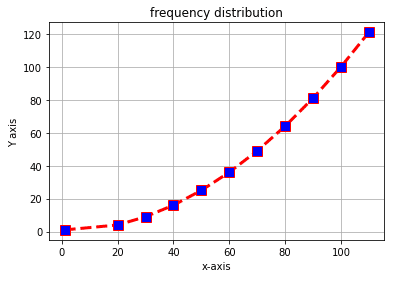
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x=(1,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110)
y=(1,4,9,16,25,36,49,64,81,100,121)
plt.plot(x,y,c='red',linewidth=3, label='line1', linestyle='dashed' , marker='s', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10)
plt.xlabel('x-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y axis')
plt.title('frequency distribution')
plt.grid('true')
plt.show()Line Graph: set X & Y Axis limit
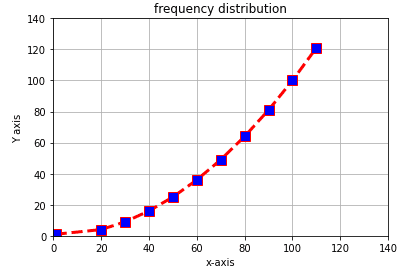
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x=(1,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110)
y=(1,4,9,16,25,36,49,64,81,100,121)
plt.plot(x,y,c='red',linewidth=3, label='line1', linestyle='dashed' , marker='s', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10)
plt.ylim(0,140)
plt.xlim(0,140)
plt.xlabel('x-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y axis')
plt.title('frequency distribution')
plt.grid('true')
plt.show()Automatic Data generation & Graph plotting
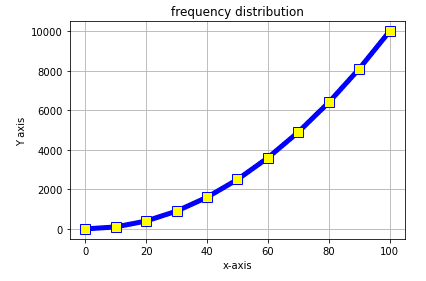
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x=np.arange(0,101,10)
y=x**2
plt.plot(x,y,c='blue',linewidth=5, label='line1', linestyle='solid' , marker='s', markerfacecolor='yellow', markersize=10)
plt.xlabel('x-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y axis')
plt.title('frequency distribution')
plt.grid('true')Plot: Two graphs on the same axis
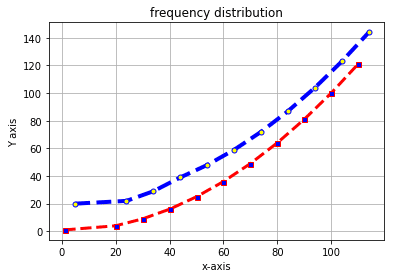
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x1=(1,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110)
y1=(1,4,9,16,25,36,49,64,81,100,121)
x2=(5,24,34,44,54,64,74,84,94,104,114)
y2=(20,22,29,39,48,59,72,87,104,123,144)
plt.plot(x1,y1,c='red',linewidth=3, label='line1', linestyle='dashed' , marker='s', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=5)
plt.plot(x2,y2,c='blue',linewidth=4, label='line2',linestyle='dashed', marker='o', markerfacecolor='yellow', markersize=5)
plt.xlabel('x-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y axis')
plt.title('frequency distribution')
plt.grid('true')
plt.show()Graph: Legends location
Legend Location: Upper-right
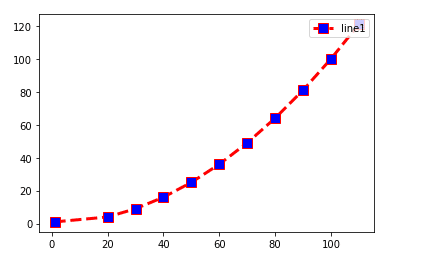
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x =(1,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110) y=(1,4,9,16,25,36,49,64,81,100,121) plt.plot(x,y,c='red',linewidth=3, label='line1', linestyle='dashed' , marker='s', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10) plt.legend(loc='upper right')
Legend Location: Upper-left

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x =(1,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110) y=(1,4,9,16,25,36,49,64,81,100,121) plt.plot(x,y,c='red',linewidth=3, label='line1', linestyle='dashed' , marker='s', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10) plt.legend(loc='upper left')
Legend Location: Lower-left
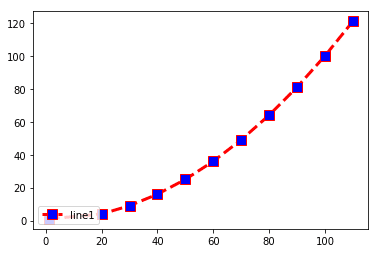
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x =(1,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110) y=(1,4,9,16,25,36,49,64,81,100,121) plt.plot(x,y,c='red',linewidth=3, label='line1', linestyle='dashed' , marker='s', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10) plt.legend(loc='lower left')
Legend Location: Lower-right
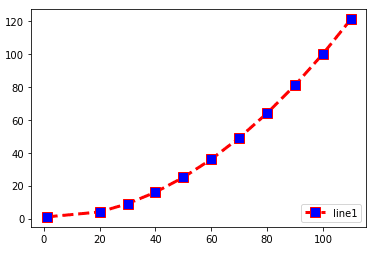
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x =(1,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110) y=(1,4,9,16,25,36,49,64,81,100,121) plt.plot(x,y,c='red',linewidth=3, label='line1', linestyle='dashed' , marker='s', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10) plt.legend(loc='lower right')
Legend Location: Center-right
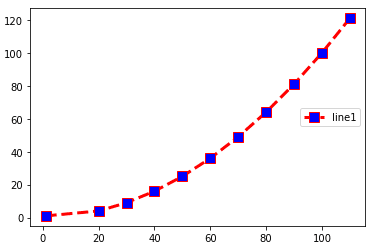
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x =(1,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110) y=(1,4,9,16,25,36,49,64,81,100,121) plt.plot(x,y,c='red',linewidth=3, label='line1', linestyle='dashed' , marker='s', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10) plt.legend(loc='center right')
Legend Location: Center
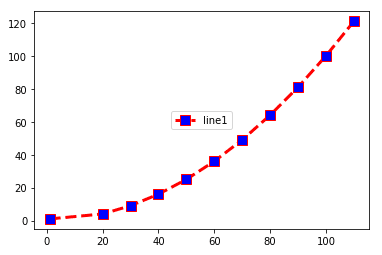
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x =(1,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110) y=(1,4,9,16,25,36,49,64,81,100,121) plt.plot(x,y,c='red',linewidth=3, label='line1', linestyle='dashed' , marker='s', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10) plt.legend(loc='center')
Legend Location: Center-left
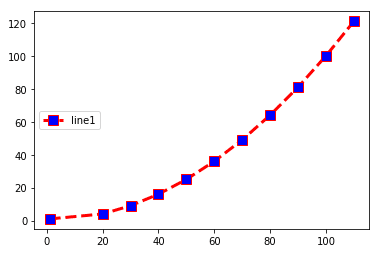
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x =(1,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110) y=(1,4,9,16,25,36,49,64,81,100,121) plt.plot(x,y,c='red',linewidth=3, label='line1', linestyle='dashed' , marker='s', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10) plt.legend(loc='center left')
Plot- Legend with maths equation
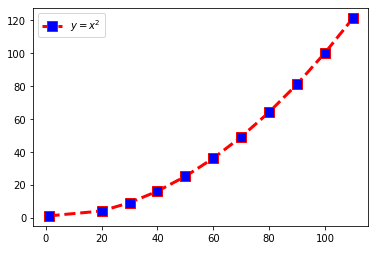
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x=(1,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110) y=(1,4,9,16,25,36,49,64,81,100,121) plt.plot(x,y,c='red',linewidth=3, label='line1', linestyle='dashed' , marker='s', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=10) plt.legend(loc='upper left') plt.legend(['$ y=x^2
Bar graph -Vertical bar
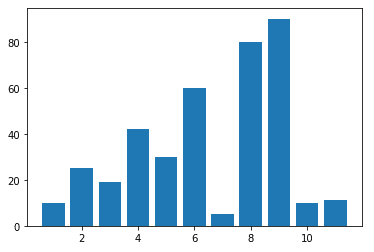
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt y=(10,25,19,42,30,60,5,80,90,10,11) x=(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11) plt.bar(x,y) plt.show()
Bar graph – Horizontal bar
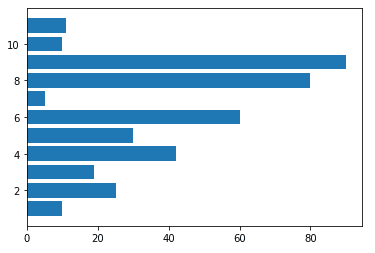
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt y=(10,25,19,42,30,60,5,80,90,10,11) x=(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11) plt.barh(x,y) plt.show()
Bar Graph – with bar description
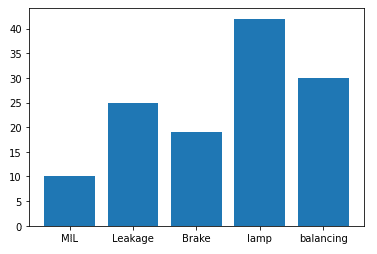
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x=('MIL','Leakage','Brake','lamp','balancing')
y=(10,25,19,42,30)
plt.bar(x,y)
plt.show()Pie chart – Normal
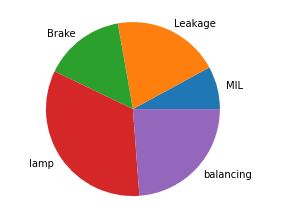
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x=('MIL','Leakage','Brake','lamp','balancing')
y=(10,25,19,42,30)
plt.pie(y, labels=x)
plt.show()Pi chart- Exploded
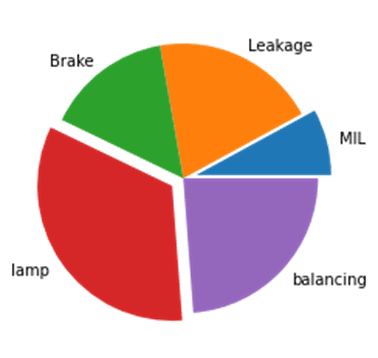
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x=('MIL','Leakage','Brake','lamp','balancing')
y=(10,25,19,42,30)
explode=(0.1,0,0,0.1,0)
plt.pie(y, labels=x, explode=explode)
plt.show()Scatter Plot
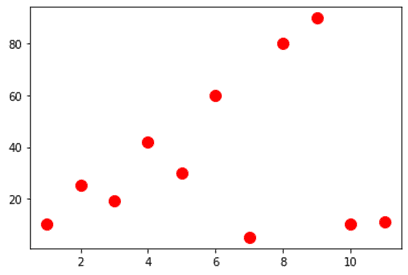
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt y=(10,25,19,42,30,60,5,80,90,10,11) x=(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11) plt.scatter(x,y,c='red',s=100) plt.show()
Scatter Plot: Colour and Point size variation(within)
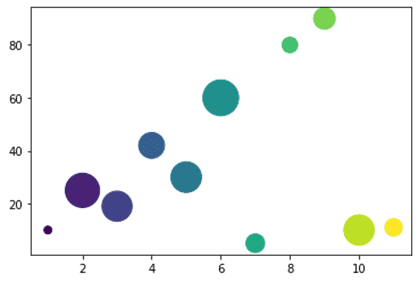
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt y=(10,25,19,42,30,60,5,80,90,10,11) x=(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11) col=np.arange(0,11,1) pwidth=np.random.rand(11)**1*1000 plt.scatter(x,y, c=col, s=pwidth) plt.show()
Scatter Plot: Color fading (alpha) effect

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt y=(10,25,19,42,30,60,5,80,90,10,11) x=(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11) col=np.arange(0,11,1) pwidth=np.random.rand(11)**1*1000 plt.scatter(x,y, c=col, s=pwidth,alpha=0.3) plt.show()
Histogram: Random number with a defined sigma value
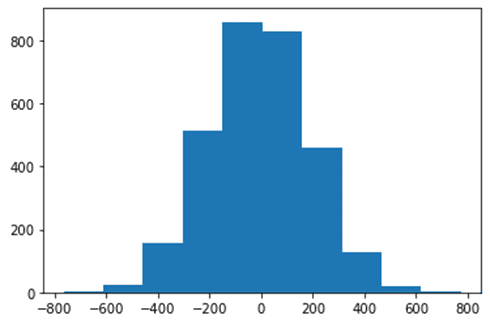
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt randomdata=np.random.normal(size=3000)*200 plt.hist(randomdata,bins=10) plt.show()
Histogram: With increased Bins
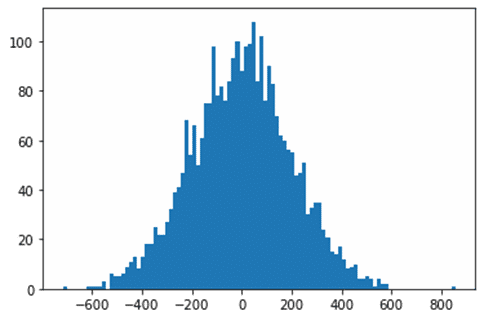
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt randomdata=np.random.normal(size=3000)*200 plt.hist(randomdata,bins=100)
Histogram: With defined class width
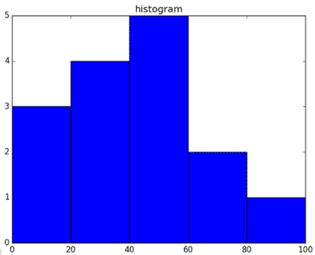
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
a = np.array([22,87,5,43,56,73,55,54,11,20,51,5,79,31,27])
plt.hist(a, bins = [0,20,40,60,80,100])
plt.title("histogram")
plt.show()Error plot ( X-error)
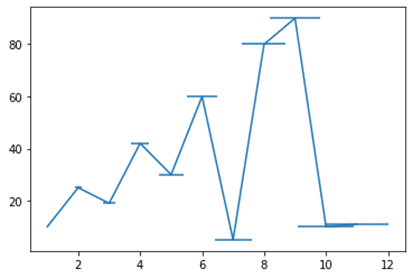
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np y=(10,25,19,42,30,60,5,80,90,10,11) x=(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11) z=np.linspace(0,1,11) plt.errorbar(x,y,xerr=z) plt.show()
Error plot ( Y-error)
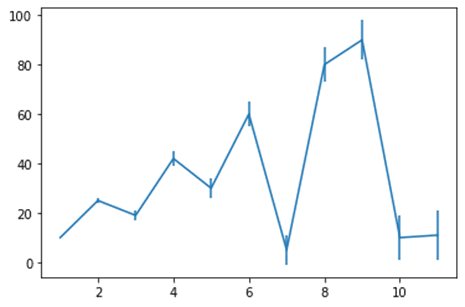
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.errorbar(x,y,yerr=z)
Sine graph
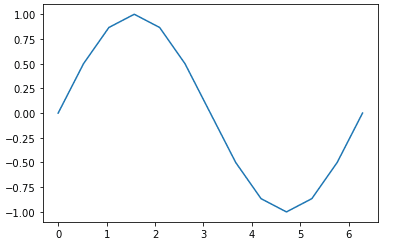
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x=np.arange(0,2*np.pi+.1,np.pi/6) y=np.sin(x) z=np.linspace(0,2,13) plt.plot(x,y)
Sine graph with Error plot
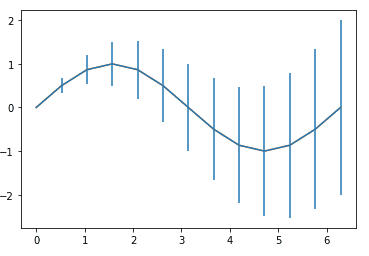
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x =np.arange(0,2*np.pi+.1,np.pi/6) y=np.sin(x) z=np.linspace(0,2,13) plt.errorbar(x,y,yerr=z) plt.plot(x,y)
Error graph : Default Marker + Cap
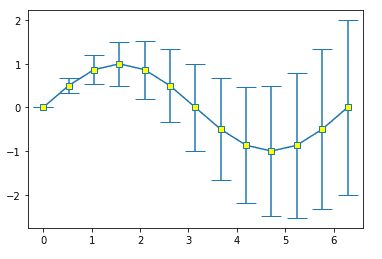
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.errorbar(x,y,yerr=z,marker='s',mfc='yellow' , capsize=10 )
Error graph : Marker(bigger) + Cap(bigger)
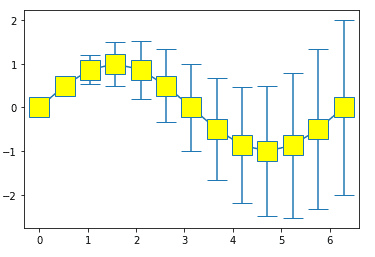
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.errorbar(x,y,yerr=z,marker='s',mfc='yellow' , markersize=20,capsize=10 )
Plot : Math equation (Y = mx + c)
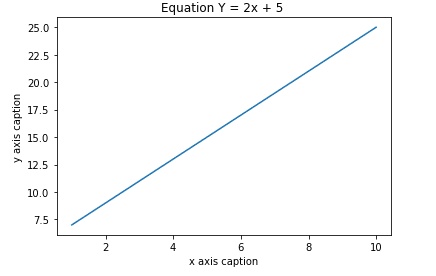
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.arange(1,11)
y = 2 * x + 5
plt.title("Equation Y = 2x + 5")
plt.xlabel("x axis caption")
plt.ylabel("y axis caption")
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.show()Plot- Sine wave
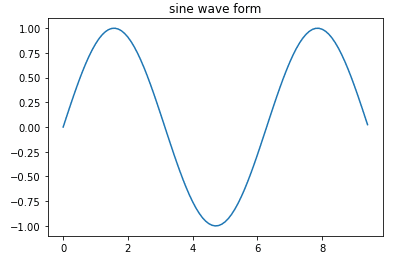
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.arange(0, 3 * np.pi, 0.1)
y = np.sin(x)
plt.title("sine wave form")
plt.plot(x, y)Two graphs: Vertical Stacking
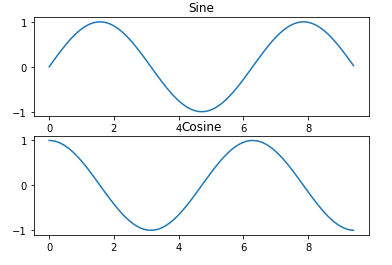
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Compute the x and y coordinates for points on sine and cosine curves
x = np.arange(0, 3 * np.pi, 0.1)
y_sin = np.sin(x)
y_cos = np.cos(x)
# Set up a subplot grid that has height 2 and width 1,
# and set the first such subplot as active.
plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
# Make the first plot
plt.plot(x, y_sin)
plt.title('Sine')
# Set the second subplot as active, and make the second plot.
plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
plt.plot(x, y_cos)
plt.title('Cosine')Three Graphs: Vertical Stacking
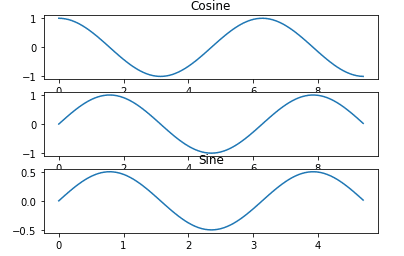
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.arange(0, 3 * np.pi, 0.1)
y_sin = np.sin(x)
y_cos = np.cos(x)
plt.subplot(3, 1, 1)
plt.plot(x, y_cos)
plt.title('Cosine')
plt.subplot(3, 1, 2)
plt.plot(x, y_sin)
plt.subplot(3, 1,3 )
plt.plot(x/2, y_sin/2)
plt.title('Sine')
plt.show()Three Graphs: Vertical Stacking
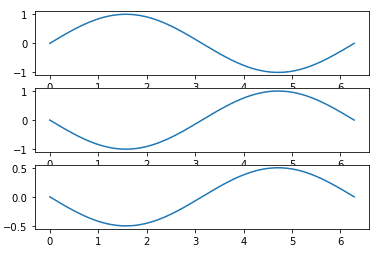
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fig, A = plt.subplots(3) x = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 400) y=np.sin(x) A[0].plot(x,y) A[1].plot(x,-y) A[2].plot(x,-y/2)
Three Graphs: Horizontal Stacking
s
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig,(A1,A2,A3) = plt.subplots(1,3)
x = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 400)
y=np.sin(x)
A1.plot(x,y)
A2.plot(x,-y)
A3.plot(x,-y/2)
fig.suptitle('horizontal stacking')Four graphs Horizontal & Vertical Stacking
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, A = plt.subplots(2,2)
x = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 400)
y=np.sin(x)
A[0,0].plot(x,y)
A[0,0].set_title('AA')
A[0,1].plot(x,-y)
A[0,1].set_title('BB')
A[1,1].plot(x,-y/2)
A[1,1].set_title('CC')
A[1,0].plot(x/10,y*0.3)
A[1,0].set_title('DD')Graph: Horizontal & Vertical Stacking in Multi-Color
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, A = plt.subplots(2,2)
x = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 400)
y=np.sin(x)
A[0,0].plot(x,y, 'tab:red')
A[0,0].set_title('AA')
A[0,1].plot(x,-y, 'tab:green')
A[0,1].set_title('BB')
A[1,1].plot(x,-y/2, 'tab:orange')
A[1,1].set_title('CC')
A[1,0].plot(x/10,y*0.3)
A[1,0].set_title('DD')Four Graphs: Horizontal + Vertical Stacking (X-axis equal span, all graphs)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, A = plt.subplots(2,2, sharex=True )
x = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 400)
y=np.sin(x)
A[0,0].plot(x,y)
A[0,0].set_title('AA')
A[0,1].plot(x,-y)
A[0,1].set_title('BB')
A[1,1].plot(x,-y/2)
A[1,1].set_title('CC')
A[1,0].plot(x/10,y*0.3)
A[1,0].set_title('DD')Four Graphs: Horizontal & Vertical Stacking (X & Y equal span, all graphs)
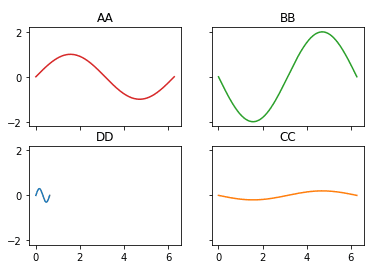
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, A = plt.subplots(2,2,sharex=True , sharey=True)
x = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 400)
y=np.sin(x)
A[0,0].plot(x,y, 'tab:red')
A[0,0].set_title('AA')
A[0,1].plot(x,-2*y, 'tab:green')
A[0,1].set_title('BB')
A[1,1].plot(x,-y/5, 'tab:orange')
A[1,1].set_title('CC')
A[1,0].plot(x/10,y*0.3)
A[1,0].set_title('DD')
Two graphs with a common X-axis
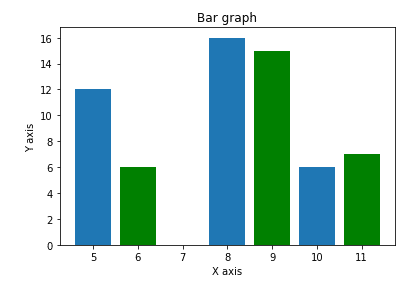
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = [5,8,10]
y = [12,16,6]
x2 = [6,9,11]
y2 = [6,15,7]
plt.bar(x, y, align = 'center')
plt.bar(x2, y2, color = 'g', align = 'center')
plt.title('Bar graph')
plt.ylabel('Y axis')
plt.xlabel('X axis')Two graphs with a common Y-axis
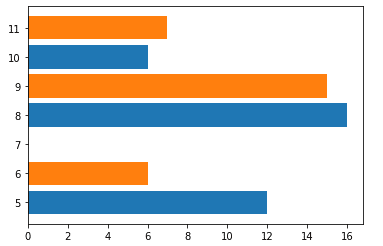
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np x1 = [5,8,10] y1 = [12,16,6] x2 =[6,9,11] y2 =[6,15,7] plt.barh(x1,y1) plt.barh(x2,y2) plt.show()
The package is available in binary distribution as well as in the source code form on

